
| Home | |
| Physics | |
| physical constants | |
| non-SI units | |
| periodic system of elements | |
| Math | |
| goniometry | |
| series | |
| expansion of functions | |
| integrals | |
| differentials | |
| various | |
| Selected topics | |
| properties of water | |
| properties of air | |
| Online calculators | |
| Various | |
| Parabolic Fit | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| Relative Humidity | |
| oF/oC Converter | |
| Various utilities | |
| Unicode generator | |
| Unicode tables | |
| General info | |
| references (incomplete) | |
| links | |
Physical properties of air
back to main menu
properties listed below:
To calculate relative humidity from dry-bulb and wet-bulb temperatures,
general
viscosity
density
try our Relative Humidity Calculator
| quantity | value |
| density (T=273 K) | 1.29 kg/m3 |
| viscosity (T=273 K) | 17.1 x 10-6 Pa s |
| specific heat at constant pressure (cp; T=273 K) | 1000 J kg-1 K-1 |
| ratio cp / cV (T=273 K) | 1.40 |
| heat conductivity (T=273 K) | 0.024 W m-1 K-1 |
| melting point (approx; p=p0) | 60 K |
| boiling point (approx; p=p0) | 80 K |
| melting heat (approx) | 2.1 x 105 J/kg |
| critical temperature (approx) | 132 K |
| critical pressure (approx) | 3.8 x 106 Pa |
| inversion temperature (approx) | 659 K |
| speed of sound | 331 m/s (T=273 K) 340 m/s (T=293 K) |
relative permittivity 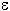 r (T=273 K; p=p0) r (T=273 K; p=p0) |
1.0006 |
| index of refraction (relative to vacuum) |
1.00029 (589 nm; T=273 K; p=p0) |
viscosity of air (online calculator) [top]
The viscosity of air, as a function of temperature, is well described by the following empirical equation, with air temperature T in Celcius [oC] and viscosity in Pascal-seconds [Pa.s]:
Error: <0.1x10-6 Pa.s; validity range: 0-54oC.
[Source: parabolic fit on values from CRC Handbook, 1986; Weast (Ed.); page F-42]
density of humid air (online calculator) [top]
The density of humid air, as a function of temperature, barometric pressure and partial vapour pressure, is well described by the following empirical equation:
T: absolute temperature [K]; B: barometric pressure [Pa]; pv: partial pressure of water vapour [Pa]; density in [kg/m3]. NB: saturated vapour pressures can be found here.
[Adapted from: CRC Handbook, 1986; Weast (Ed.); page F-8]
Holsoft (c) 2001
email: